Accessibility in Meetings
/prod01/cdn-pxl-elginedu-prod/media/website/site-assets/images/hero-banners/accessible-meetings-hero.jpg)
Making a meeting accessible involves creating an environment where everyone, including individuals with disabilities, those who speak languages other than English, those with diverse learning styles, and many others, can fully participate and engage. Here are some key steps to ensure that a meeting is accessible:
1. Consider the Physical Environment
-
Venue Accessibility: If the meeting is in person, ensure the location is physically accessible for people with physical and visual disabilities. This includes ramps, elevators, wheelchair-accessible restrooms, clear and unobstructed pathways (e.g., no loose cables across walking areas), and appropriate seating arrangements.
-
Clear Signage: Use clear and visible signs to direct participants to key areas such as the meeting room, restrooms, exits, and elevators.
-
Lighting: Ensure that the room is well-lit. Ensure that participants can view the projected materials on the screen without glare from the sun.
-
Sound: Ensure that the room is acoustically appropriate. Ensure microphones are used if the room is large. If you are reserving a room through ECC’s Facilities Rental department, the event host may request microphones. In the following rooms on campus, the event host may request assistive listening devices (ALDs) in addition to the microphones:
- B180 Heritage Room
- B181 Community Room
- B182 Alumni Room
- E121 Dining Room
- E125 Seigle Auditorium
- Building J Event Center
The ALDs may be beneficial for people who are hard of hearing, allowing them to better hear the speaker. For the ALD to work, the speaker must use the microphones in the room and should pass the microphone to other panelists and participants who are asking a question.
- Noise: Limit unnecessary background music when speakers are presenting. If the hallway is noisy, close the door to reduce distractions.
2. Provide Accessible Digital Materials
-
Use Accessible Formats: Design meeting materials (e.g., slides, documents, promotional flyers) in accessible formats, such as:
-
Text-based documents (excluding PDFs and images) that assistive technology (e.g., screen-reading software) can read.
-
-
Follow Accessibility Guidelines: Ensure that any documents or slides adhere to accessibility guidelines (e.g., use of proper headings and alternative text for images). For tips on incorporating accessibility guidelines into your materials, visit the Accessibility web page.
- Presentation Materials: Enhance the readability of your materials by using:
- Good contrast colors when adding text to your slides.
- 200-point font or larger, and
- Sans-serif fonts, such as Arial and Calibri.
3. Offer Multiple Ways to Participate
-
Virtual Meetings: Utilize a platform that offers accessibility features, including live captioning, screen reader compatibility, and keyboard shortcuts. Tools like Zoom, Teams, and Google Meet often offer closed captioning or real-time transcription. Utilize platforms that are compliant with the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) to ensure accessibility for individuals with disabilities.
-
Hybrid Meetings: For hybrid settings (in-person + virtual), ensure that remote participants can see and hear everyone clearly. A good microphone and camera setup are essential.
-
Provide Written Options: Allow participants to communicate in various ways, including audio, video, and/or chat, in case they are unable to speak or prefer written communication.
4. Provide Communication Access
-
Sign Language Interpreters: If requested, arrange for a sign language interpreter for participants who are deaf or hard of hearing.
-
Real-Time Captioning/Transcription: Utilize real-time captioning tools or provide a transcription of the meeting for individuals who are deaf or hard of hearing afterward. To use real-time captioning/transcription during an in-person meeting:
- Complete the Facilities Rental Request Form.
- Please indicate that you would like to have access to microphones and Zoom capabilities in the room. You may request a room that has built-in microphones in the ceiling. If the meeting room does not have built-in microphones in the ceiling, you may request that a Zoom cart be placed in the room. You may request that IT conduct a sound check before the meeting starts.
- Before the meeting starts, log in to the computer in the meeting room or on the Zoom cart in the room.
- Log in to Zoom.
- Left-click on the icon for "CC." If you do not see the "CC" button, click on "More" and select "Captions."
- To adjust the size of the captions, left-click on the "^" symbol next to the "CC" button to select "Caption Settings." Adjust the font size from small to large. Click on the "X" at the top right.
- Left-click on "Transcript."
- Unmute the microphone in Zoom when the meeting starts.
-
Language Accessibility: If participants speak different languages, consider offering translation services or providing materials in multiple languages to ensure accessibility.
5. Ensure Flexibility in Scheduling
-
Time Zone Sensitivity: Schedule meetings at times that are accessible to people across different time zones.
-
Allow Time for Breaks: If meetings are long, incorporate regular breaks to accommodate participants with attention or health concerns.
- Test Your Technology: Test the platform, materials, and accessibility features (e.g., captions, screen reader functionality) to ensure everything works smoothly.
7. Provide Clear Agenda and Instructions
-
Share an Agenda: Before the meeting, provide an agenda in a clear and accessible format. This extra step allows participants to review the content and request accommodations or other support in advance.
8. Market Your Accessibility Options
- Invitation: In your meeting invitation, specify which built-in accessibility features are available (e.g., captioning).
- Accommodation Request Statement: Include a statement about how participants can request accommodations or assistance. Here is a sample statement that the event host may include on flyers, announcements, and other materials to advertise the event:
- ECC strives to host inclusive and accessible events that enable all individuals, including those with disabilities, to engage fully. If you require reasonable accommodations to participate in this meeting or event fully, please contact (email address and phone number) at least one week before the meeting/event.
- Food: If food is being served, clearly indicate allergens and other options (e.g., gluten-free, vegan, vegetarian, etc.).
9. Foster an Inclusive Culture:
-
Encourage Inclusivity: Create a culture where participants feel comfortable sharing their needs. For example, encourage people to let you know if they need any specific accommodations.
-
Be Mindful of Communication Styles: Be aware that some people may need extra time to respond or may prefer different forms of communication (e.g., written rather than spoken).
- Provide Printouts of Handouts: Use appropriate font size (minimum of 12-point font) and type (e.g. Arial, Calibri) for handouts.
- Verbal Descriptions: Verbally describe visual materials (e.g. slides, charts, graphs).
10. Post-Meeting Accessibility
-
Follow Up: After the meeting, provide meeting notes, transcriptions, or recordings in accessible formats for those who may have missed parts of the meeting or need extra time to review the content.
-
Feedback Mechanism: Ask for feedback from participants about the accessibility of the meeting and any improvements that could be made for future meetings.
Zoom
How to make a Zoom meeting accessible
- Enable live transcription to provide captions for participants who are deaf or hard of hearing. Refer to these instructions on enabling the live automatic captions in Zoom
- Share meeting materials in advance so that everyone has time to review them.
- Use a clear and slow speaking pace to ensure everyone can follow along.
- Allow participants to use the chat feature to ask questions or share comments without interrupting.
Google Meet
How to make Google Meet meetings accessible
- Ensure that all participants have the link to the meeting well in advance.
- The live captions are enabled for Google Meet meetings. Participants may turn on the captions by clicking on the "CC" button on the bottom of their screen.
- Share relevant documents and materials before the meeting to allow everyone to prepare.
- Encourage the use of screen readers or other assistive technologies by providing necessary support.
Microsoft Teams
How to make Microsoft Teams meetings accessible
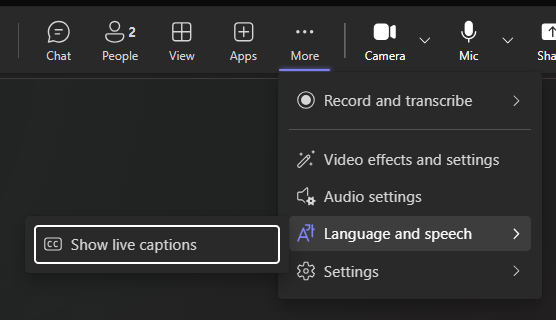
- Use live captions to provide real-time text for participants who are deaf or hard of hearing.
- Share agenda and materials before the meeting to help everyone prepare.
- Encourage the use of the chat feature for questions or comments to promote engagement without interruption.
- Ensure that the meeting layout is clear and easy to follow, allowing participants to pin important speakers.